
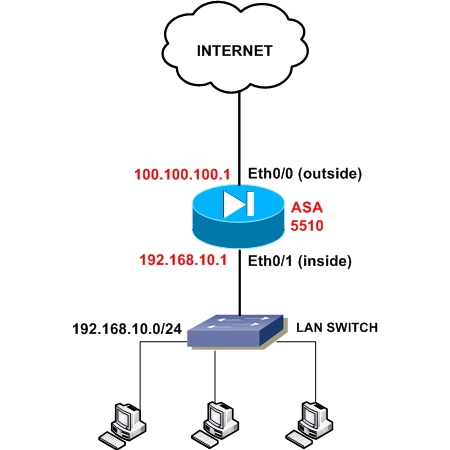
Native VLAN Modification of VLAN The default VLAN is always VLAN 1, and it can’t be changed. The native VLAN is also useful when we deal with VoIP.ĭifference Between Default VLAN and Native VLAN By default, the native VLAN is VLAN 1, but it can be changed to any number such as VLAN 10, VLAN 20, VLAN 99, etc. That is, the native VLAN detects and identifies traffic coming from each end of a trunk link. The 802.1Q trunk port assigns untagged traffic on a native VLAN.
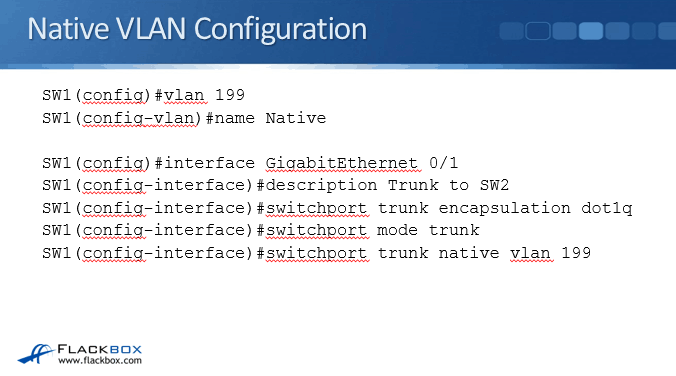
The native VLAN is per trunk per switch configuration. A native VLAN is defined in 802.1Q (it supports untagged traffic while inter-switch link doesn’t support untagged traffic.) trunk port standard which supports traffic coming from several VLANs as well as the traffic that doesn’t come from a VLAN. For Cisco and some other vendors, VLAN1 is the default VLAN.Ī native VLAN is a special VLAN whose traffic traverses on the 802.1Q trunk without any VLAN tag.
Because of this, any device connected to any port can communicate with other devices on other switch ports. All these ports engage in the default VLAN which makes all of them a part of the same broadcast domain. In Default VLAN all switch ports turn into a member of the default VLAN just after the initial bootup of the switch. Difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission.nslookup command in Linux with Examples.
#CISCO ASAV CHANGE NATIVE VLAN PORT HOW TO#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
